Electric Flux and Gauss's Law
Electric Flux and Gauss's Law: Overview
This topic explores the meaning and importance of electric flux. It also highlights the gauss's law related to electric flux. We will also explore some applications of gauss law and learn how to find the electric field due to infinite wire.
Important Questions on Electric Flux and Gauss's Law
Explain in case of charged spherical shells, Graph is discontinuous while Graph is continuous.
Find the variation of electric field strength E with increase in distance r from the centre of a hollow conducting sphere.
Which one of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field strength E with distance r from the centre of a hollow conducting sphere?
What is the electric field inside a charged conductor ? Plot a graph between electric field strength and distance from centre in case of a charged conducting sphere of radius .
E signifies the _____ passing through a certain area dS. is the total amount of charge and signifies the permittivity of the vacuum.
Derive Gauss's law from Coulomb's law.
The solid angle is a dimensionless quantity.
Supplementary physical quantities are physical quantities which do not depend on other physical quantities like fundamental physical quantities.
Supplementary physical quantities are physical quantities which do not depend on other physical quantities like fundamental physical quantities.
_____ is the S.I unit of electric charge.
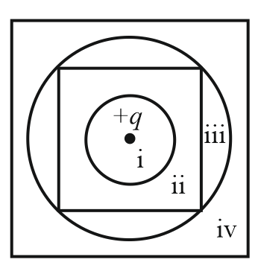
Figure shows, in cross section, two Gaussian spheres and two Gaussian cubes that are centered on a positively charged particle. Select the correct alternatives.
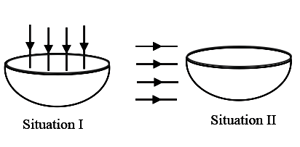
In the figure, a hemispherical bowl of radius is shown. Electric field of intensity is represented in each situation by direction lines.
The flux entering and leaving a closed surface and respectively. Net charge enclosed by this surface in is
Name the SI unit of solid angle.
An electron is moving around an infinite linear charge in a circular path of diameter . If linear charge density is and the speed of the electron is written as, then find accurate up to two digits after the decimal point. (, )
Angle formed at the top of a cone is an example of ‘Plane Angle’.
State Gauss' theorem in electrostatics and write its expression.
The electric potential at the surface of a charged spherical conductor of radius is . Electric potential at its centre in volt is
An electron of energy is fired from a distance of perpendicularly towards an infinite charged conducting plate. What should be the minimum charge density on plate so that electron fails to strike the plate?
A large uniformly charged sheet having a surface charge density of lies in plane. Calculate the electric flux through a circular loop of radius whose axis makes on angle of with axis.
